5.5 KiB
Extend tim-vx with customized operator
tim-vx will provide two different approches supporting extend AI operators besides built-in ops.
- Compose new operation with builtin ops. example: RNNCell
- Register opencl kernel as customized operator
User stories
As application developer, I want to be able to create new opeartor with built-in ops, so that I can simplify the lowing from high-level framework(tensorflow,pytorch) to tim-vx, since I don't want to rewrite same pattern in different frameworks.
As application developer, I want to be able to create my own opeartor with standard opencl kernel, so that I can support novel operators not presented in tim-vx.
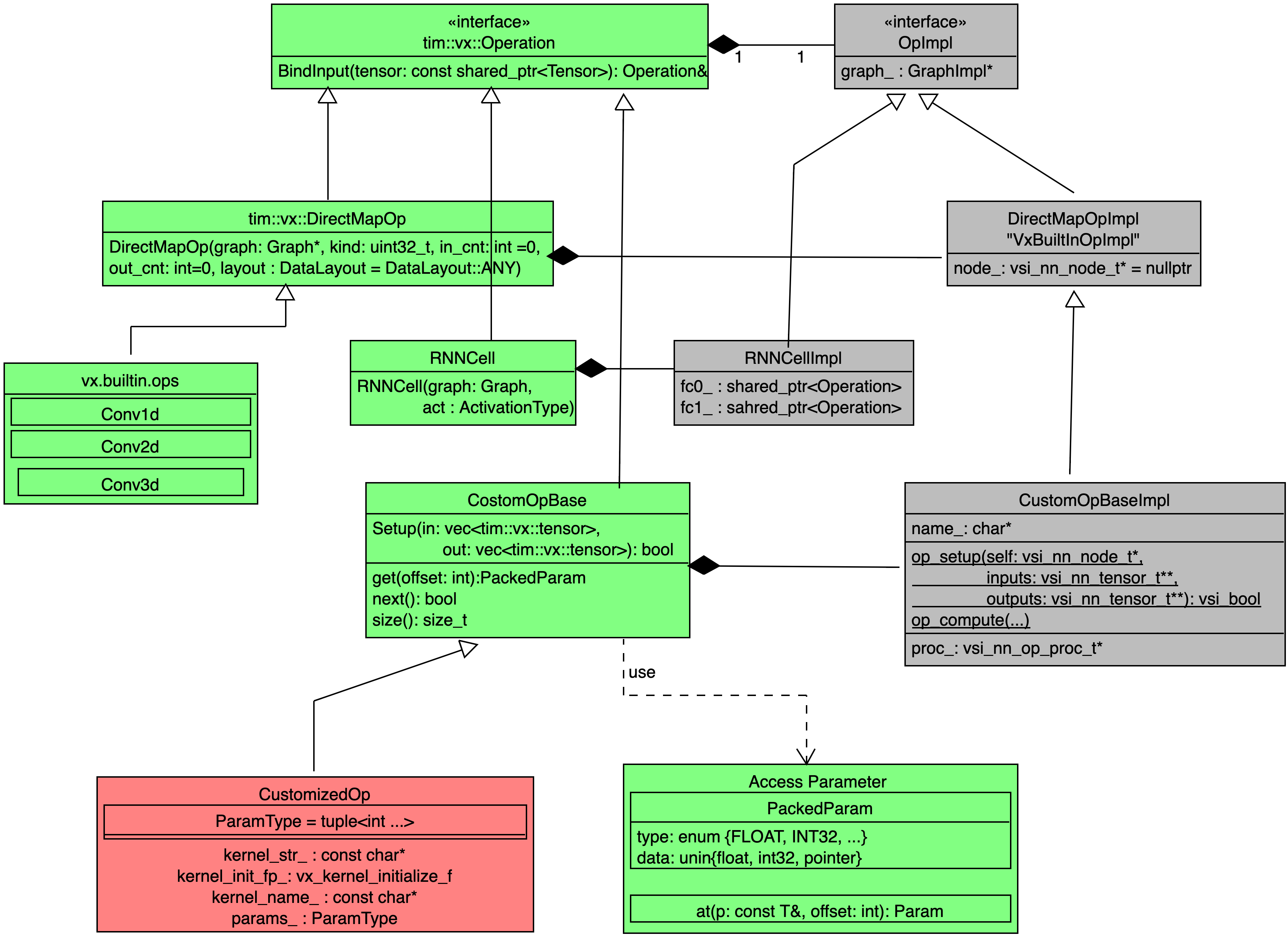
Design overview
- Green components implemented as a public API of tim-vx.
- Red components could be implemented outside of tim-vx.
- Gray components implemented as a private code inside tim-vx.
Composed operator
If some operator can be composed by built-in operators, such as RNNCell which actually built from FullyConnected, Tanh, and DataConvert Layers, developer can add their own operator implementation before VSI introduce high-performance built-in ops.
Implementation reference of RNNCell
Keynotes for RNNCell:
In the constructor of RNNCellImpl, internal operators - fc/tanh/dataconvert - will be created without inner connection. The inner connection build up inside bindInput() and bindOutput();
Layout Inference {todo}
Inside of composed operator, it actually is a subgraph of tim-vx's built-in operatos, it should be easy to extend the original layout inference for build-in operators to composed operator - just do layout inference inside the subgraph.
void ComposedOp::OnInputs(std::vector<std::shared_ptr<vx::Tensor> next_tensor) {
for(auto op: op_->OpsInSubgraph()) {
auto Cloned = handleLayoutInference(new_graph, op);
}
}
Customized opencl operator
Customzied kernel should implemented with standard OpenCL 2.0; With tim-vx built-in infrastructure, user can inject their operator with :
- OpenCL kernel stream as source code;
- Kernel enqueue configuration for global_work_size and local_work_size;
- Scalar parameter list defined as a std::tuple;
- Readable operator name;
TIM-VX provide two different approach to integrate user's operator:
- Build from source : build tim-vx source and user operators' implementation as single library;
- Build from sdk: tim-vx prebuilt as a standalone library and a set of standard headers; user build operator implementation and link with tim-vx;
From tim-vx api view, the customized operator registed at graph-level, the registration automatically effected at the first time to create instance of the customized operator. With this approcah, user can override built-in operator or support new operator in a new model easily.
void CreateGraphWithCustomizedOperator() {
// create context/graph/tensor as before.
auto conv = graph->CreateOperation<tim::vx::Conv2d>(...);
auto post_detect = graph->CreateOperation<3rd_party::DetectionPostProcess>(...);
post_detect.BindInput(...);
post_detect.BindOutput(...);
graph->Compile();
}
How to determine parameter list in a tuple
Usually, kernel take two different kinds of paramter: "tensor-like" and scalar; The tensor-like parameters usually is the output-tensor from other operators or input for other operator. In the operator's paramter list, only scalar parameters should be defined. "tensor-like" operand should provied by bindInput/bindOutput.
The scalar paramters MUST provided at kernel registration.
Take following hswish as example: CL kernel signature:
__kernel void hswish_F32toF32(
__read_only image2d_array_t input,
__write_only image2d_array_t output,
float inputScale,
float inputTail,
float outputScale,
float outputZP)
C++ paramter list defined by user
namespace user {
class customized_hswish : public tim::vx::CustomizeOpBase {
using param_types = std::tuple<float/*inputScale*/, float/*inputTail*/, float/*outputScale*/, float/*outputZP*/>;
customized_hswish(std::shared_ptr<tim::vx::Graph> g, const param_types& params/* any other parameter required by c++ code, not relevant to cl kernel*/) {
}
auto clone(std::shared_ptr<tim::vx::Graph> g) {
return g->CreateOperation<user::customized_hswish>(g, this->params/*others*/);
}
};
}
How to config global_work_size and local_work_size
Similar feature as clEnqueueNDRangeKernel in standard OpenCL;
Some tips for work_size: HWThreadCount = 4
Layout Inference {todo}
so far we don't support this feature. User should take care of the layout transform carefully. TODO: vsi will rework the framework so that any customized op can work properly in layout transform.